- Home
- Super Fruits
- Health Benefits of Blueberries
What are the Health Benefits of Blueberries?
Intro | Wild Vs Cultivated | Blueberries and Their Antioxidants | Health Benefits | What are Anthocyanins Good For? | Precautions | Shop
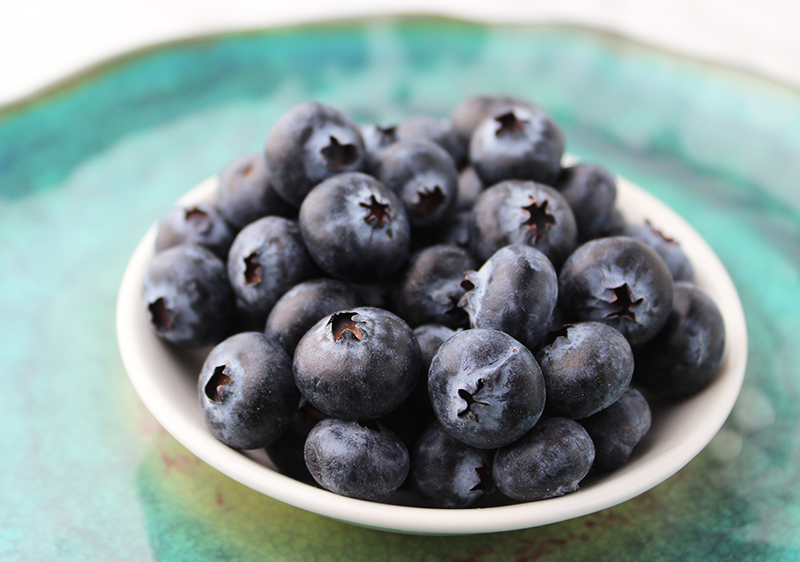

Blueberries are a small round blue berry with a white, purple to light yellow-green colored flesh and are related to cranberry, bilberry and huckleberry. The wild blueberry species is native to the colder climates of North America.
Indigenous cultures in these regions used the entire blueberry plant from leaves to roots and called the berries "star berry" because of the flared five-pointed star-like pattern on the top of the fruit. This is the location where the white bell-shaped blossoms once formed.
Wild Vs Cultivated
Table of Contents
Intro | Wild Vs Cultivated | Blueberries and Their Antioxidants | Health Benefits | What are Anthocyanins Good For? | Precautions | Shop
For most of human history, all blueberries on earth were
wild-sourced. Their domestication first occurred in the state of New
Jersey in the early 1900s with extensive farming developing in the
1940s.
The cultivated type is a bit different than wild blueberries, however. Wild berries (Vaccinium angustifolium) are a lowbush blueberry that grows low to the ground.They are typically smaller with a more purple flesh.
The cultivated highbush blueberry (Vaccinium corymbosum) is a taller plant and the one most common in commercial fruit production and can range quite a bit in size depending on the cultivar.

Wild blueberries sold on a large scale are often called "semi-wild" as these ecosystems are often managed to encourage natural growth.
What are the unique health benefits of blueberries that often give them the superfruit label?
Blueberries and Their Antioxidants
Blueberries are nutritionally speaking most famous for their higher amounts of ANTIOXIDANTS relative to other foods. These antioxidant constituents come from polyphenols, flavonoids and vitamin-based sources.
In essence "anti" oxidants inhibit the oxidation of other molecules, a chemical reaction that can manifest "free radicals." This effect causes a chain reaction to occur which may damage cellular tissue and DNA structure. Antioxidants can offer a shielding influence that essentially neutralizes these harmful substances which can contribute to aging and disease.
Along with a well-balanced diet and healthy lifestyle practices, one of the best ways to increase antioxidants in the body is through dietary choices.
Blueberries, especially wild-sourced, produce fruit with concentrated levels of antioxidants, like polyphenols which collectively function to defend the plant and the fruit itself. (Source) This develops a hardy and resilient berry that is extremely high in these protective nutrients when consumed.
In research comparing blueberry, blackberry and strawberry, blueberries were shown to have "the strongest total antioxidant capacity."
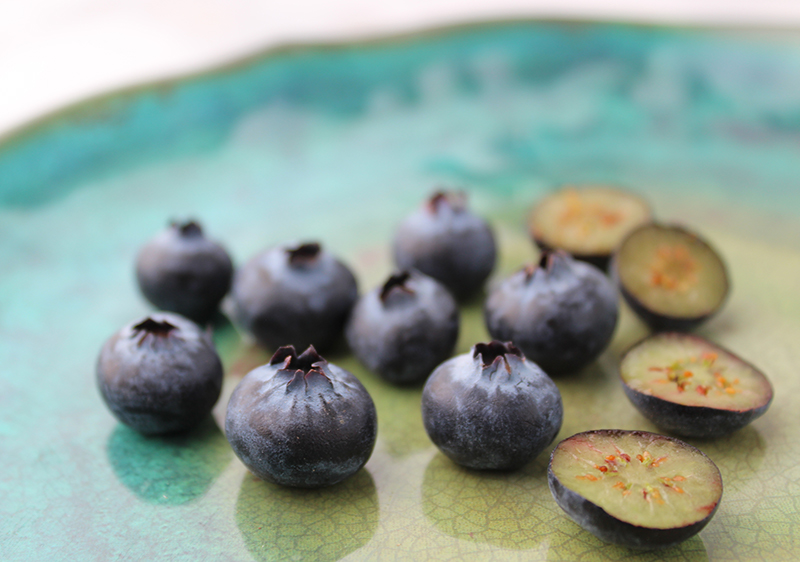

Health Benefits of Blueberries and Anthocyanin Content
Hidden directly under the skin of the fruit, the blueberry is packed with antioxidant polyphenolic compounds known as ANTHOCYANINS (*) which make up about 60% of total polyphenols.
Blueberries are one of the few foods that have a natural blue color and this is one of the main health-enhancing compounds responsible for its blue and sometimes purple-blue pigmentation.
Although anthocyanins are present in many fruits and vegetables with a red, purple and blue color, blueberries are known to contain a greater quantity and variety. This includes delphinidin and cyanidin and glucoside derivatives such as malvidin, petunidin and peonidin.
While the total anthocyanin content in blueberries can vary depending on many factors, it has been reported to range from 25 mg to 495 mg per 100 grams (or about 2/3 a cup) of ripe blueberries.
Other polyphenolic flavonoids and acids in blueberries that possess antioxidant activity are catechin, epicatechin, myricetin, quercetin, chlorogenic acid, ellagic acid and gallic acid. Like cranberries, blueberries also contain the proanthocyanidins known to be beneficial for the urinary tract.
Blueberries, as well as blackberries, are a popular fruit selection but other lesser-known anthocyanin-rich superfruits in this category include maqui, bilberries, blackcurrant, chokeberries and of course the famous acai berry.
While either wild or cultivated blueberries can be a great addition to the diet, the wild variety is known to be slightly higher in antioxidants like anthocyanins. Moreover, because wild are smaller you're also going to get a greater ratio of skin to fleshy pulp. And that's where these all-important nutrients are found.
Fresh organic blueberries are widely available, especially during the warmer seasons. When selecting your berries look for the white waxy coating which helps to preserve freshness and prevent mold.
In off-seasons, blueberries can be found as a frozen variety. They’re also one of those fruits that's sometimes freeze-dried and sold as a concentrated powder to add to blended drinks.
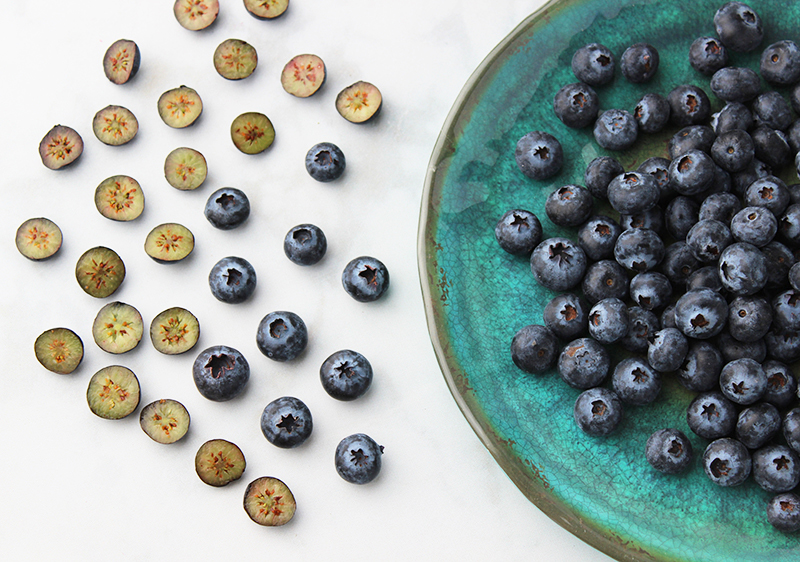

What are Blueberry Antioxidants and Anthocyanins are Good For?
While the bioactivity of anthocyanin metabolites is still undergoing
research, daily blueberry consumption of about 1/3 C (usually less than 50 mg
anthocyanins) is generally considered beneficial for mitigating the risk
of common diseases.
The health benefits of blueberries are often claimed to be good for influencing:
1) Brain and Cognitive Functions - Blueberries, along with walnuts, turmeric, and cacao are on the list of "brain foods" considered supportive to memory (*) and other cognitive functions. (*) This is due to its high antioxidant levels and anti-inflammatory properties. (Source)
2) Diabetic and Digestive Support - Blueberries are an often recommended low-sugar fruit option for diabetics. (*) According to some research, including dietary anthocyanin food sources like blueberries may help to lower the risk of type 2 diabetes. A 1/2-1 cup serving size of blueberries in the morning can also help to promote bowel regularity due to the berry’s high PECTIN fiber content.
3) Cardiovascular Health - Consuming a diet with a good amount of fruits and vegetables is considered a heart-healthy plan for proper cardiovascular function. Blueberries themselves have been reviewed as an anthocyanin-rich food for promoting such a goal. Antioxidants also help to foster optimal cholesterol levels by protecting against oxidative damage in this organ system.
4) Immune Response - Dietary antioxidants can help to assist the immune system by fighting against the daily influx of potential pathogens. Blueberries also contain immune-supportive antioxidant nutrients like vitamin C, vitamin E, beta-carotene as well as minerals like manganese, copper, zinc and iron. They are relatively high in VITAMIN C with a one cup serving averaging about 14.4mg or 24% of the Daily Value (based on a 2,000 calorie adult diet).
Precautions:
Blueberries are known to be safe to consume for most individuals but should be avoided if you have allergic reactions to foods with salicylates. Consult your nutritionist or health practitioner before consuming blueberries if you are pregnant, nursing, taking prescription medications or if you have a serious medical condition.
Shop Related Products (About Affiliates & Amazon Associate Paid Links)
Affiliate Disclaimer: This section contains affiliate product links. If you make a purchase through our recommended links, we receive a small commission at no additional cost to you. Thanks for the support.