- Home
- Herbs and Spices
- Black Pepper Vs White
Black Pepper Vs White, Main Differences Between Them
Species | Ripeness | Seed Vs Berry | Flavor | Intensity | Nutrition | Folk Uses | Piperin Use |Oxalates | Quality | Precautions | Shop
1) Same Species Piper nigrum
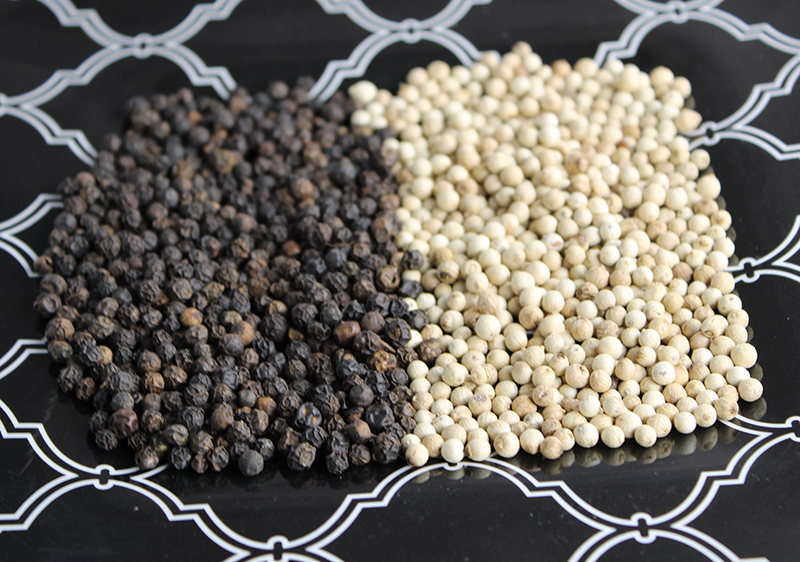

When comparing black pepper vs white there are some major differences, however the species source is not one of them.
Both white pepper and black come from the vine-growing pepper plant known as Piper nigrum.
Each of these types are also considered fruits or commonly called berries, although they contain little flesh or sweetness.
2) One is Ripe and One is Not
Table of Contents
Species | Ripeness | Seed Vs Berry | Flavor | Intensity | Nutrition | Folk Uses | Piperine Use | Oxalates | Quality | Precautions | Shop
Pepper is one of the most commonly used staple spice seasonings utilized worldwide in many home kitchens. Yet, do you know the differences between the two main varieties?
When you look at both white and black pepper side by side you might think that black is actually made from fully ripe berries. It is not. Fresh black peppercorns are harvested when the fruit is unripe and still green.
White pepper, on the other hand, is harvested when red and fully ripe.

3) Seed Vs Whole BERRY
Peppercorns are botanically known as "stone fruits" or drupes. This means they have a center seed, although a bit smaller than the typical stone fruit varieties like cherries or peaches.
White pepper actually comes from this seed. Processing is achieved by removing the red ripe thin outer skin via a method called retting. This technique involves soaking the berries which loosens the flesh layer. This exposes the naked white seed of the berry that is then dried and used ground or whole for "cracked pepper".
In contrast, black pepper is sourced from the whole unripe green berries that are briefly heated in hot water to sterilize and get them ready for drying. This cooking technique breaks down the skin cells and promotes enzymatic browning.
The final drying process causes it to turn a dark black color and produces a wrinkled looking peppercorn appearance, whereas white peppercorns have a signature smoothness.
Black pepper actually contains the white seed. This is the reason why when ground or cracked it is specked with white flakes.

4) Flavor Profile Comparison
To a sensitive culinary palette, there is a big difference when it comes to the flavor profile of each variety.
Black pepper seems to be the favorite herbal spice for overall taste diversity, especially when freshly cracked in a pepper grinder.
Black pepper is hotter and spicier than white pepper due to the higher piperine content found in the skin. Likewise, fresh black pepper has an undeniable flavor complexity over white adding a pungent, woodiness with notes of pine, citrus and a hint of sweetness.
This is why it’s the often-preferred choice among cooks around the world.
White pepper with its mellow heat and earthier taste can be more suitable for those with sensitivities to hot spices. It is warming but not overpowering and sometimes a better choice for aesthetic purposes when you don't want dark flakes of pepper in mashed potatoes, chowders or gravies.
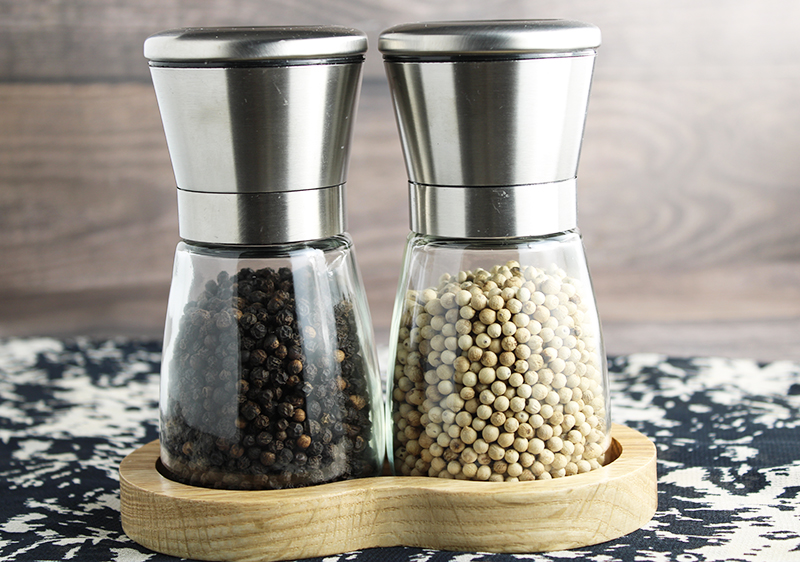

5) Taste Intensity
Again, both black pepper and white pepper are more intense, flavorful and aromatic when freshly ground from the peppercorn. That's why they're often sold whole in plastic grinder bottles.
We don't however recommend using these plastic types long term as microplastics can tend to contaminate as the plastic degrades from use. Purchasing a good glass or wood grinder with a ceramic or stainless steel blade is way better and a worthy investment for your pepper, as well as coarse salt, grinding needs.
In addition, when considering black pepper vs white, it is important to note that the flavor of black lasts way longer because it’s made from the whole berry with the skin included. This helps to preserve freshness and the sharp taste. White pepper by comparison can lose flavor quite rapidly, especially when ground and/or exposed to light.
Pre-ground tabletop pepper of both types will typically degrade faster, losing aroma and taste qualities.
6) Nutritional Considerations
The key nutritional component in peppercorns is the compound known as PIPERINE. Piperine from the Piper Genus is recognized for its anti-inflammatory and antioxidant potentials.
Black pepper is especially piperine-rich because higher concentrations are found in the outer skin layer or pericarp of the whole berry. It can thus be a good way to get more of these healing properties into your diet.
White pepper does contain some piperine, but in much smaller amounts.
7) Popular Folk Uses
When it comes to popular folk uses, generally black pepper is the star of the show over white which is considered less medicinal in value.
Black pepper is not only higher in piperine but is also full of essential oils such as limonene, copaene, caryophyllene, sabinene and pinene isomers. (*)
It is also found to contain larger amounts of myristicin, the essential oil present in nutmeg known for its slight psychoactive influence.
It is acknowledged by science as an antibacterial and antimutangenic due to its two major active phytocompounds piperine and copaene. This goes along with some of its other long held traditional uses as an antimicrobial and antiseptic agent.
As an herbal stimulant and carminative, it has been utilized throughout the ages as a digestive and circulatory aid, helpful at boosting metabolism and opening natural detoxification pathways.
It is likewise a popular ingredient to blend with other herbs for constipation issues. Its warming properties are also believed to offer therapeutic potential for things like achy joints.
Black pepper is frequently used alongside long pepper in Ayurvedic formulations specifically for removing dampness and clearing up congestion, two aspects beneficial for Kapha imbalances.

8) Piperine Use in Supplement Formulas
The piperine component in black pepper is extensively used in the commercial supplement industry because it helps to enhance the absorption of certain nutrients or active compounds found in other herbs and foods.
You therefore may find black pepper and/or piperine as an ingredient in formulated supplement extracts like curcumin or turmeric as well as ashwagandha. As an added component it helps to improve overall bioavailability of these and many other substances.
9) Black Pepper Contains Oxalates
One of the lesser-known downsides of black pepper is that it is higher in oxalate content compared to other herbs and spices. This is because it includes the outer skin which is where they are most concentrated.
Usually, one teaspoon of ground black pepper can contain about 16mg of OXALATES. This amount can be higher when freshly cracked.
For those on a low oxalate diet, you may want to consider white pepper which is much lower because it's composed of only the seed of the berry.
10) Peppercorn Quality
The quality of peppercorns can vary according to the cultivar. Tellicherry and Malabar, both from the Malabar coast region of India, are the two most popular and each known for their particular flavor nuances.
White peppercorns may also differ in taste and texture depending on the retting process utilized. Some manufacturers may soak them for shorter periods than others which produces a more robust and spicier taste.
Precautions:
An excess of white or black pepper can aggravate those sensitive to hot spices. Consult your nutritionist or health professional before use if you are pregnant, nursing, have a serious health issue or are taking any medications.
Shop Related Products (About Affiliates & Amazon Associate Paid Links)
Affiliate Disclaimer: This section contains affiliate product links. If you make a purchase through our recommended links, we receive a small commission at no additional cost to you. Thanks for the support.